When data packets are lost during network transmission, they fail to reach their destination. Packet loss happens when data transmission is slowed down due to network congestion, hardware problems, software bugs, and other factors.
High packet loss is one of three major network performance issues, the others are latency and jitter. These are all nightmares for PC gamers. In this article, you'll understand the meaning of packet loss, what causes packet loss, and how to avoid it.

Part 1: What's the Meaning of Packet Loss?
Part 2: How Much Packet Loss Is Normal?
Part 3: What Causes Packet Loss?
Part 4: 5 Fixes for Packet Loss in Gaming
What's the Meaning of Packet Loss?
Everything we do on the internet is done in packets. Consider "Packet" as packing for a trip the same way you would for a vacation: you'd put everything you'd need in a backpack, carry-on, or checked-in suitcase.
The network shrinks packet size and encrypts the packets before they set out on their journey in order to fit all the data in and move data quickly from point A to point B. In keeping with the luggage comparison, this is comparable to how you might stuff as much as you can before securely locking your suitcase by using packing cubes, vacuum packs, or even rolled-up clothes inside your shoes.
Unfortunately, it's a sad reality that occasionally, when you travel, your checked luggage will miss its connection, get scratched or wet by rain on the runway, or just plain vanish between points A and B. The digital superhighway's packets follow the same rules. Some data packets may experience delays, damage, or even loss during their journey from one location to another. That's called packet loss.

How Much Packet Loss Is Normal?
Before answering the question "how much packet loss is normal", many of you may wonder whether packet loss is normal. I have to say it depends.
Cisco recommends that packet loss on voice over IP (VoIP) traffic be kept at or below 1% in their quality of service (QoS) tutorial. This is regarded as acceptable because there wouldn't be any service issues if only 1% of all packets involved in a SIP VoIP call were lost.
However, this does not imply that you should accept packet loss, particularly when it comes to real-time applications. Any packet loss above 2% in these circumstances will cause problems for users, resulting in jittery VoIP conversations or missed shots when playing online multiplayer games like Call of Duty or PUBG. This may aggravate end users and, in the latter scenario, result in unintended player churn.
What Causes Packet Loss?
Now that we understand the meaning of packet loss and how much of it can be regarded as normal instead of high packet loss, it is time to make one step further and find out the causes of high packet loss. Generally speaking, like other issues in gaming, packet loss is caused by network issues, hardware issues, software issues, etc.
A congested network connection
Network congestion, also known as bandwidth congestion, means that when your Internet bandwidth can't handle the amount of current data it's meant to process, VoIP call quality and overall transmission speed suffer. Consider it a digital traffic jam just like you are facing every day to work.
Due to link congestion and heavy traffic, some information packets are left behind to give the network time to "catch up," which causes your data to take longer to reach its intended location. In most cases, when the network congestion eases, these packets will automatically reappear. However, occasionally, a packet may get permanently lost in the mix.
Incompatible or corrupted hardware
Routing or firewall issues are the most frequent hardware issues that result in packet loss. Inadequate computing resources, outdated firmware, or defective hardware could be to blame for the failure. Assume your luggage's zipper broke in the middle of your journey. There will undoubtedly be some spillage along the way.
Software issues
Data transfer requires the use of business communication software, which when malfunctioning can also result in packet loss.
Unexpected behavior may occur on your network if software stutters as a result of a programming mistake. Software flaws or a failure to update the software when prompted are frequently to blame for this. Think of it as, along your trip, the luggage was mistakenly labeled to another destination by the airline company. This can also happen to the data packets.
5 Fixes for Packet Loss in Gaming
Fix 1: Use a packet loss checker & fixer
To begin with, I suggest you use a packet loss checker to test your real-time packet loss rate in gaming. After having a better understanding of your current packet loss situation, can you find a proper way to fix it? LagoFast is your best option to do these works. It's not only capable of testing your real-time packet loss while gaming but also knows how to fix high packet loss. LagoFast has more than 8 years of experience in fixing in-game packet loss, lagging, and high ping and has received a great amount of applause from users all over the world.
The features of LagoFast are as follows:
- Offer a Plan-Per-Minute Service
- Capable of testing packet loss in gaming
- Effectively fix high packet loss
- More than 8 years of experience in fixing all kinds of game issues
Although its functions are powerful, LagoFast is quite easy to use, here're the instructions:
Step 1: Download LagoFast
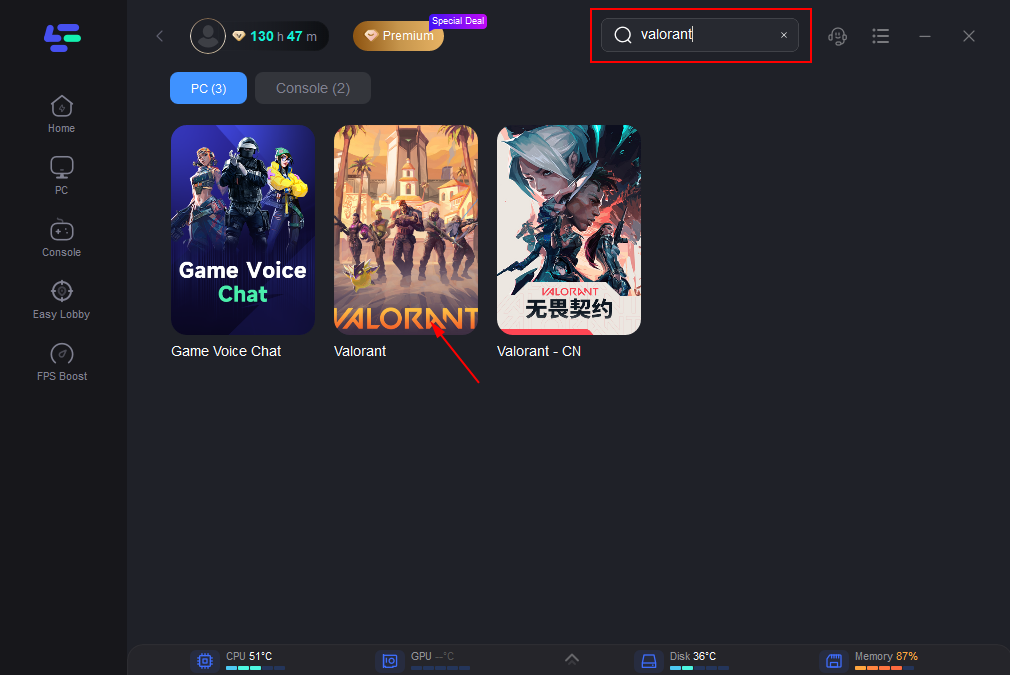
Step 2: Type the name of your game in the Search box and select it from the search results. (Here I take Valorant as an example.)
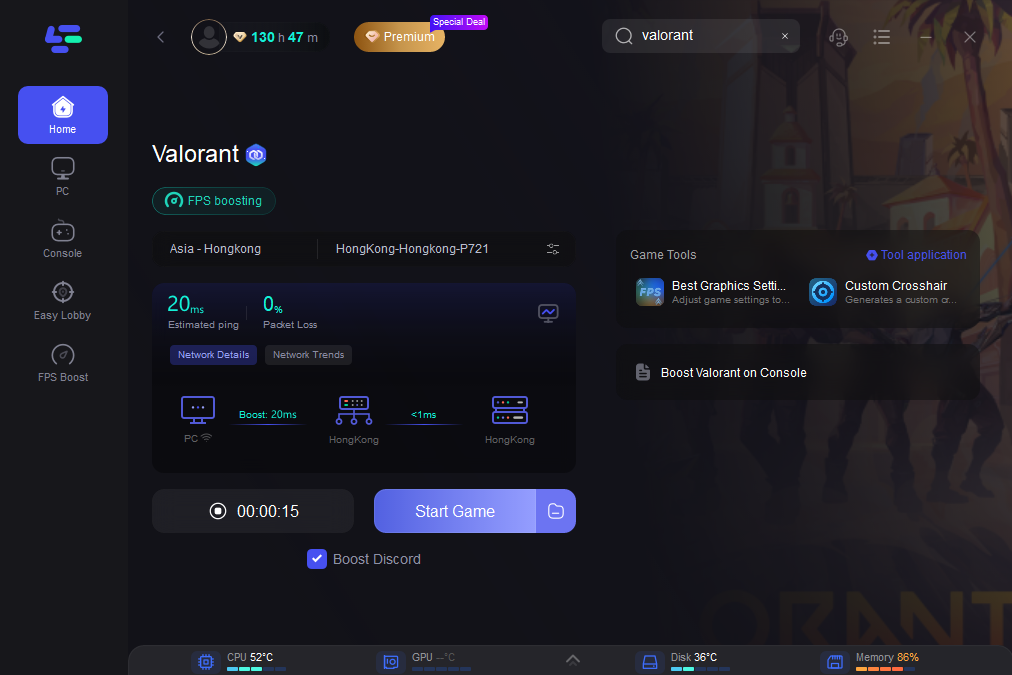
Step 3: Click the Boost button to start boosting.
On the next page, you can see your real-time ping rate and packet loss rate. And it'll start fixing if the rates are too high.
Fix 2: Improve your hardware
Make sure you're using new equipment whenever possible because working with outdated equipment can also result in packet loss. If you find the brand-new equipment is too expensive, you can buy them second-handed, which is much cheaper.
When your hardware consistently breaks down, shows "error" messages, shuts down unexpectedly, or simply stops functioning as it should, it's time to upgrade it.
Packet loss can be reduced by maintaining a dedicated IT team to update VoIP and server hardware.
Fix 3: Always upgrade your software in time
Software that hasn't been updated in a while may consume too much network bandwidth, leading to packet loss and other performance problems.
In spite of the fact that it's best to enable automatic updates, you should always manually update your software as soon as you receive a notification.
Restart the application and restart your hardware after the software has been updated (or if there haven't been any updates).
You might need to wait for the development team to publish a fix if the software still has known bugs. On the other hand, if a quick fix is unavailable, think about using an alternative software program that doesn't result in packet loss.
Fix 4: Change to a better network connection
Wi-fi isn't the best option for VoIP connections, as was previously mentioned, but if it's the only option available, it might be the cause of packet loss.
If your signal is weak or intermittent, try restarting the router or device to see if it improves. If not, use a Wi-Fi analyzer to determine if the problem is in the Wi-Fi settings.
If necessary, configure your device to connect to another Wi-Fi network, or better yet, use a wired connection.
Fix 5: Avoid network congestion
Packet loss can result from bandwidth congestion, which occurs when your network is unable to cope with the high volume of the current traffic.
To resolve this, monitor your network performance to ascertain whether congestion results from a high volume of outbound data at a particular time of the day.
If at all possible, pick a less busy time. Although scheduling calls and conferences for off-peak hours may not be as simple with VoIP communications, it is a possibility.
Next, set traffic priorities to ensure that the most crucial data is sent across the network first which improves data flow and decreases congestion.
If the problem is still unfixed, contact your ISP to change your plan. Broadening your bandwidth can fundamentally fix the network congestion.

Boost Your Game with LagoFast for Epic Speed
Play harder, faster. LagoFast game booster eliminates stutter and lags on PC, mobile, or Mac—win every match!
Quickly Reduce Game Lag and Ping!
Boost FPS for Smoother Gameplay!